Osteoma is a chronic disease of the spine whose root cause is degenerative changes of the discs. With the progression of the disease, other structures of the spine also participate in the pathological process - the vertebral body, intervertebral disc joints, ligaments, etc. v.
The disease affects people of all ages. Until recently, osteosarcoma was considered common in the elderly, but recently an increase in its incidence in young people has been revealed. Both women and men get the disease equally often.
Why does osteonecrosis occur?
To better understand what osteonecrosis is, it is necessary to briefly understand its causes and mechanisms of occurrence.
The formation of pathological changes in osteonecrosis of the spine is gradual. Many years often pass from the onset of the pathological process in the disc cartilage to the appearance of the first symptoms of osteonecrosis.
Causes of osteonecrosis
The health of the spine is directly affected by many negative factors. If their influence is carried out for a long time, then the result of this is the appearance of pathological changes in the structure of the spine. And this contributes to the formation of osteonecrosis.
For example, people who lead a sedentary lifestyle, and those who are overweight know the process of bone loss. Excessive physical activity, back and neck injuries, some somatic diseases can also lead to the development of this pathology. And aggravated by heredity and old age are direct factors leading to the development of degenerative damage to the cartilage tissue of the disc.
How does osteonecrosis develop?
The developmental (or pathogenesis) mechanism of osteonecrosis is controversial and has not been fully studied. Most likely this disease is formed on the basis of a metabolic disorder that occurs in the structures of the spine.
Under the influence of adverse factors, irreversible changes often occur in the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral disc, followed by gradual destruction (or destruction).
The pathological process then also spreads to the bony tissue of the vertebrae with its deforming development and irreversible changes in the surrounding structures.
The appearance of such changes in the intervertebral disc directly depends on its anatomical nuances:
- Cartilaginous tissue does not have its own blood supply system. Its nutrition is provided by the bone tissue of the adjacent vertebrae. Therefore, in the case of circulatory disorders due to insufficient or, conversely, excessive physical stress on the spine, cartilage nutrition is also affected.
- There are also no nerve fibers in the cartilage. Therefore, with functional overload of the intervertebral disc, the transmission of a nerve impulse that activates the metabolism will not be timely.
- The disc's ability to self-heal (regenerate) cartilage tissue is slowed down due to its structural features.
There are also other factors that clearly contribute to the development of degenerative processes in the cartilage tissue of the disc and the formation of osteonecrosis.
Stages of pathological change
Based on current data on the pathogenesis of this pathology, several stages of the degenerative process in the intervertebral disc can be conditionally distinguished. Stages of osteonecrosis of the spine:
- Primary. Cartilaginous tissue of the intervertebral disc undergoes structural changes under mechanical impact - its dysfunction occurs. Characterized by the appearance of cracks on the disc surface, varying in size and depth. These cracks are then transformed into protrusions (hernias).
- Intermediate. It is characterized by the appearance of instability of the affected area of the spine due to pathological mobility of the vertebrae. In this case, one of the main functions of the spine, the protective function, is disturbed. The neural tubes and blood vessels that run in its bony tubules become vulnerable. Vivid clinical symptoms of the disease develop.
- Limited. There is a replacement of the affected cartilage tissue with a coarser and denser fibrous tissue. At the same time, herniated discs also disappeared. And the pathological mobility of the vertebrae is replaced by a marked limitation of their mobility. There is often a narrowing of the spinal canal with the development of manifestations of compression of the segments of the spinal cord.
Therefore, each stage of the disease is characterized by the appearance of its own specific symptoms, which certainly plays an important role in the selection of treatment methods for osteonecrosis.
Clinical Manifestations
Signs of osteochondrosis of the spine appear as changes in the bony tissue of the vertebrae. The patient may not have any complaints for quite a long time.
The disease is characterized by a chronic course, with alternate periods of exacerbation and remission.
Usually, exacerbation of osteonecrosis occurs under the influence of provoking factors: physical overstrain, hypothermia, prolonged exposure to an uncomfortable position, for example, in a dream or atworkplace, etc. v.
There are many symptoms of this disease, depending on the localization of the pathological process and the severity of structural changes in cartilage and bone tissue. All of these symptoms can be grouped into several syndromes. Quite often they are combined with each other.
lens syndrome
It occurs in most patients with osteonecrosis of the spine. In the occurrence of this syndrome, compression (compression) of the spinal nerve roots due to the pathological structure of the spine plays a role.
The main sign of milia syndrome is pain, which in some cases is capable of spreading (irradiation) along the covering of the respective root. Characterized by pain that radiates from top to bottom. For example, if the lumbar region is affected, the buttocks hurt and for the legs.
Pain intensity increases with body or neck rotation, physical activity. Pain sensations are characterized as cutting, pulling, baking.
In addition, along with the pain syndrome, in the affected area often develop symptoms of a violation of sensitivity in the form of hyperesthesia, as well as disturbances of sensitivity, numbness.
If the disease is advanced and the cause of compression cannot be eliminated, desensitization is substituted with desensitization (desensitization), often accompanied by loss of function of the affected spinal roots.
spinal syndrome
This syndrome develops due to compression of the spinal cord. The most common cause of such compression is a herniated disc.
Increasingly decreased sensitivity, response to temperature and painful stimuli. Progressive muscle weakness develops in both the limbs and trunk. Symptoms of paralysis or paralysis are often formed.
Vegetative Vascular Syndrome

This syndrome most often develops in the localization of the cervical and cervical vertebrae of the spinal cord.
The cause of vascular disorders in osteonecrosis is reflex constriction or mechanical compression of large vessels passing in the bony canals of the spine. In this case, various symptoms may develop, resembling circulatory disorders due to ischemia of the brain or the main arteries of the extremities. This is often the cause of diagnostic errors.
In addition, various vegetative disorders often develop. They are most pronounced in women (emotional ease, sleep disturbances, menstrual irregularities, etc. ).
visceral syndrome
It is characterized by the occurrence of pain in the heart, organs of the gastrointestinal tract, etc. Often such patients are treated for a long time and completely unsuccessfully for any somatic diseases. .
For example, if the thoracic region is affected, pain behind the sternum may occur, similar to those of angina. Often there is a reflex to feel the heartbeat.
Diagnostic principles
In addition to the characteristic symptoms, additional examination methods play an important role in disease identification and staging - X-rays of the spine, computed tomography, and magnetic nuclei.
As indicated, other methods are performed, for example, electroencephalogram, electrocardiogram, Doppler vascular scan, etc. v.
Treatment of osteonecrosis
Spinal osteolysis is an integrative approach. When choosing one or another treatment method, it is necessary to evaluate the extent of damage to the spinal structures, the nature and severity of the clinical manifestations, as well as the stage of the disease (acute orremission).
Preventive measures also play an important role in the treatment of cervical spondylosis in order to reduce the frequency of exacerbations and preserve the structure of the vertebrae and discs.
Tactics during the level up
An important condition to treat the disease in this stage is to give the affected spine a rest. To do this, the patient is assigned to bed rest with the use of various devices to immobilize the affected vertebral segment.
In some cases, hospitalization in the neurology department is required.
Medical treatment
To reduce the intensity of pain in osteonecrosis, various drugs are prescribed:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs);
- analgesic;
- muscle relaxants.
In the absence of an effect of their use, it is recommended to prescribe an internal blockade of the affected area using a local anesthetic.
With cervical localization of osteonecrosis, circulatory disorders of the brain often develop. To reduce such manifestations, drugs are prescribed to improve cerebral blood flow. In addition, it is necessary to use drugs to treat symptoms - reduce nausea and vomiting, improve vestibular disorders, etc. v.
In addition, it is advisable to prescribe vitamin preparations (especially of group B), antioxidants and some others.
Physiotherapy procedures
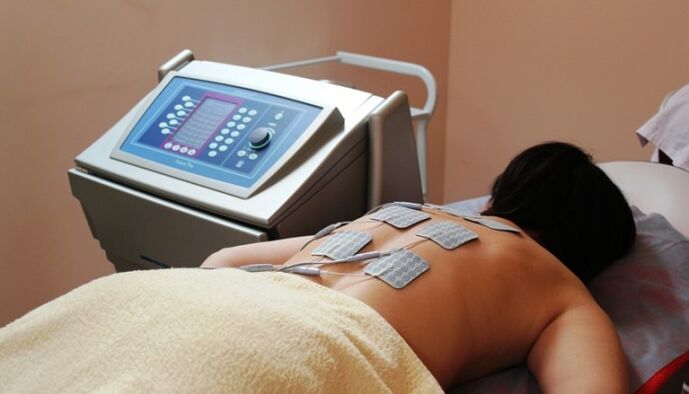
With osteonecrosis, treatment with physical factors has been widely applied. Various physiotherapeutic methods are used both during the exacerbation and in the period of remission of the disease:
- In the acute phase, ultraviolet irradiation, electromagnetic therapy (UHF), diadynamic current, etc. are used.
- In the period of remission, electrophoresis with various drugs, thermal conduction, ultrasound and other types of balanced therapy are prescribed.
Tactics in remission
After the acute manifestations of the disease subside, the treatment of the disease continues. The aim of this therapy is to reduce the frequency of exacerbations and promote the regeneration of bone and cartilage tissue of the spine.
The drug treatment prescribed for the acute phase of the disease continues. During this period, it is possible to use chondroprotectors - agents that help improve the condition of the cartilage.
In addition to physical therapy methods, massage exercises and physiotherapy are also applied.
Massage

The main effect of massage is to improve blood circulation in the affected area and strengthen the muscle corset. In addition, the professional performance of massage movements allows you to relieve muscle spasms, which often accompany this pathology.
That is why massage should be performed by a specially trained professional who is well versed in this treatment method. Improper or improper massage can lead to the development of complications or an exacerbation of the disease.
Therapeutic Exercises (LFK)
Specially selected and dosed physical exercises form the basis of exercise therapy. The complexity of such exercises is selected by the doctor individually for each patient. The principle of choosing therapeutic mobilization exercises is to reduce the physical load on the affected spine area.
The effect of physiotherapeutic exercises is to improve blood supply and lymphatic flow to the affected area, strengthen muscle tissues.
These exercises should be done every day. Often, at first, individual or group classes are held with an instructor, after which the patient can perform the exercises independently at home.
Prevention of exacerbations
Measures to prevent exacerbations of osteonecrosis of the spine are aimed at eliminating all provoking factors:
- It is necessary to monitor the correct posture and posture when standing and sitting for a long time.
- It is helpful for cases of prolonged static stress (for example, working on a computer) to take regular breaks during which you should warm up or do exercises recommended by your doctor.
- Hypothermia should be avoided.
- It is important to sleep properly with osteonecrosis, to take care of the sleeping place - the mattress and pillow. Ideally, they should be orthopedic.
- It is imperative to reduce excess body weight and timely correct concomitant endocrine and somatic pathologies.
And when the slightest symptoms of spina bifida appear, you should not delay seeing a doctor. After all, the earlier osteonecrosis of the spine is treated, the better the outcome.













































